
Debit vs. Credit Cards: What Is the Difference?
Debit and credit cards are two common plastic payment methods to choose from when you pay for something. While both offer convenience and ease of transactions both online and at your favorite retail stores, they operate on different principles and serve distinct purposes.
The biggest difference between credit and debit cards is how you access funds and manage payments. A debit card is linked to a checking account, allowing you to spend only the money you have available. On the other hand, a credit card extends a line of credit, allowing you to borrow money up to a predetermined limit.
Understanding the differences between debit vs. credit cards can help you improve your financial literacy and make more informed decisions about your money. Keep reading to learn more about credit vs. debit cards and how they work.
What Is a Debit Card?
A debit card pulls funds from your checking account. It lets you conduct electronic transactions, make purchases and withdraw cash from ATMs. You can get a debit card from a bank or credit union by opening up a checking account.
When you make a transaction or buy something with a debit card, the money is immediately taken out of your bank account.
There are a few types of debit cards available, including:
- Standard debit card: This is the most common type of debit card. It provides access to the funds in the linked checking account and can be used for purchases wherever the card network is accepted.
- Prepaid debit card: Prepaid debit cards aren’t linked to a traditional checking account. Instead, you load funds onto the card in advance by transferring money from a bank account or adding cash at retail locations.
- Electronic Benefits Transfer (EBT) cards: EBT cards are issued by state governments to distribute benefits like food stamps (SNAP) or cash assistance (TANF). Those with these cards can use them to purchase eligible items at authorized retailers.
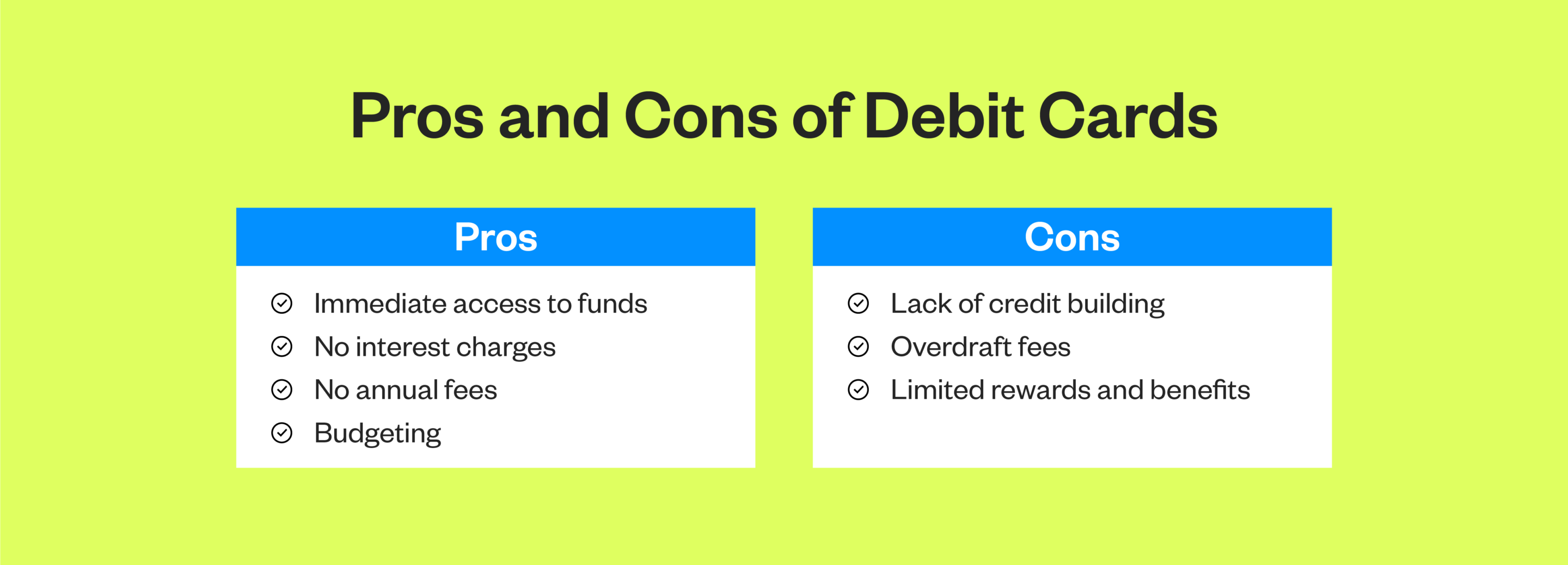
Pros of Debit Cards
Debit cards offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice for many consumers, such as:
- Immediate access to funds: With a debit card, funds are readily available for use as they are directly linked to your bank account. This means no waiting period or approval process is required, allowing for instant transactions at any time
- No interest charges: Unlike credit cards, debit cards use funds already available in your linked checking account. As a result, you don’t incur interest charges on purchases made with a debit card
- No annual fees: Debit cards don’t impose annual fees for card usage. This fee-free structure reduces the expenses associated with managing finances and ensures you can access your money without additional financial burden
- Budgeting: Debit cards facilitate effective budgeting by letting you track your spending in real-time. With instant access to transaction information through online banking platforms or mobile apps, you can monitor your expenditures, set spending limits and make informed financial decisions
Cons of Debit Cards
While debit cards offer numerous benefits, they also come with some drawbacks you should be aware of:
- Lack of credit building: Debit cards don’t contribute to building credit since they don’t involve borrowing money
- Overdraft fees: If a transaction exceeds the available funds in the linked checking account, resulting in a negative balance, your bank or credit union may charge overdraft fees
- Limited rewards and benefits: Debit cards typically offer limited rewards and benefits compared to credit cards
What Is a Credit Card?
A credit card is another payment card. But unlike a debit card, cardholders borrow money from the credit card issuer up to a predetermined credit limit to make purchases or transactions. Credit cards give you access to a line of credit that can be used for purchases, cash advances, balance transfers and other transactions.
When a purchase is made with a credit card, the cardholder is borrowing from the issuer, with the obligation to repay the borrowed amount within a specific period to avoid interest charges.
There are several types of credit cards, including:
- Basic credit card: This is the most common type of credit card, offering a revolving line of credit that allows you to make purchases up to your credit limit. Basic credit cards typically come with a variety of features and benefits like introductory offers on interest rates and balance transfers. These may be subject to annual fees
- Rewards cards: Rewards credit cards offer incentives like cashback, points or miles for qualifying purchases made using the card. You earn rewards based on your spending patterns, which can be redeemed for various rewards, including travel, merchandise, statement credits or gift cards
- Secured credit cards: Secured credit cards are designed for those with limited or damaged credit histories who may have difficulty qualifying for a traditional credit card without a good credit score. These credit cards require a security deposit as collateral. Secured cards help you build good credit by responsibly managing your credit accounts and making timely payments
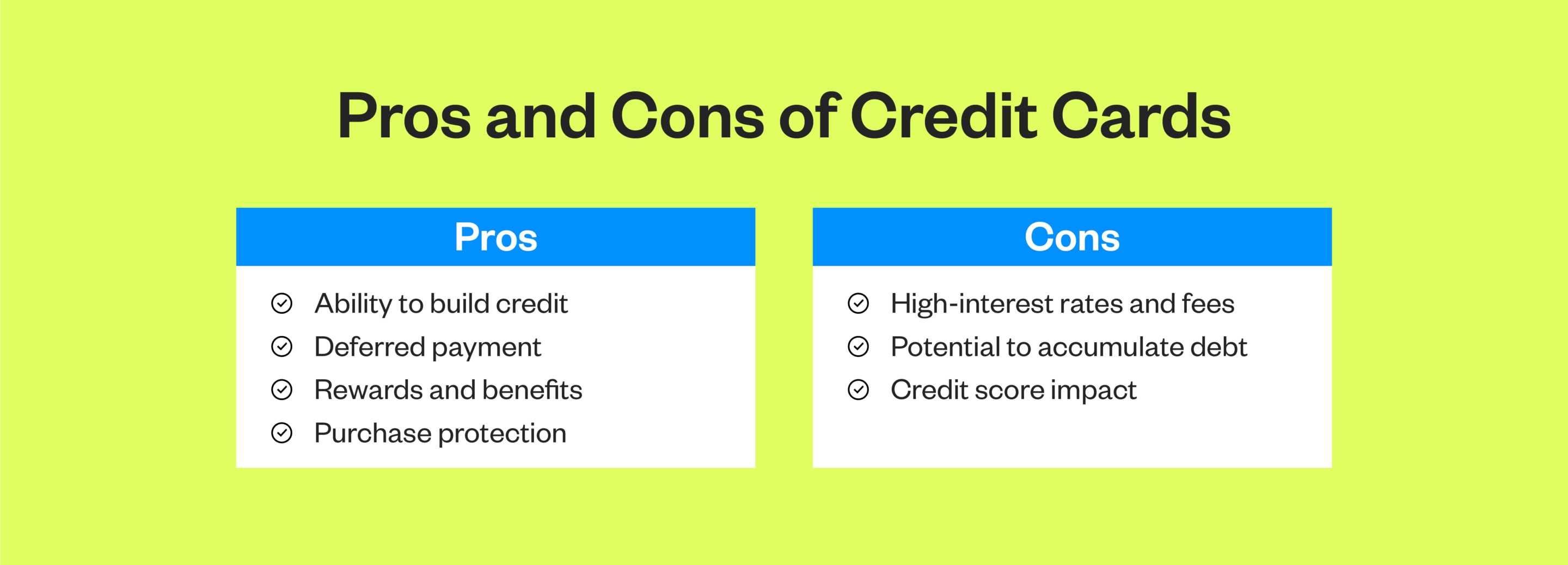
Pros of Credit Cards
Credit cards offer numerous advantages, making them a popular choice for those looking for flexibility. These benefits include:
- Ability to build credit: Responsible credit card use, like making timely payments and managing credit utilization, can help you establish and improve your credit history over time. This process can help strengthen credit scores over time, resulting in access to better loan terms when needed
- Deferred payment: Unlike debit cards, credit transactions allow cardholders to postpone payments until the end of the billing cycle. This gives you short-term financing options for purchases and more time to manage your cash flow
- Rewards and benefits: Rewards can take various forms, such as cashback, points, miles or discounts on purchases. Credit cards also offer benefits like extended warranties, travel insurance and more
Cons of Credit Cards
While credit cards offer convenience, they also come with potential disadvantages, such as:
- High interest rates and fees: If your credit card carries a balance, you may incur interest charges, especially if you have a high annual percentage rate (APR) or fail to pay the full statement balance on time. Credit cards often impose various fees, including annual fees, late payment fees, cash advance fees and balance transfer fees, all of which can increase the cost of using credit
- Potential to accumulate debt: Since credit cards provide access to a revolving line of credit, there’s a risk of overspending in occurring debt. Without careful budgeting, you may find yourself trapped in a cycle of debt, making minimum payments and occurring interest charges that can take years to pay off
- Credit score impact: While responsible credit card usage can help build credit history and improve credit scores, mismanagement or defaulting on credit card payments can lead to negative consequences. Late payments, high credit utilization and applying for multiple credit cards within a short period can lower your credit score
- Fees: Credit cards are sometimes subject to annual or monthly fees
What Are the Differences Between a Debit vs. Credit Card?
When considering a debit card vs. a credit card, it’s essential to understand how they operate and their respective features. Let’s explore key distinctions between the two types of payment methods.
Funding source
Debit cards are connected to your checking account, drawing funds from the available balance in the account whenever a transaction is made.
In contrast, a credit card uses borrowed funds from the card issuer. When using a credit card, the cardholder is essentially taking a short-term loan from the issuer to complete the transaction.
Payment process
With a debit card, transactions are processed immediately, and funds are deducted from the linked checking account right away.
On the other hand, credit card transactions involve borrowing money from the card issuer. You’ll receive a monthly statement detailing your purchase and outstanding balance. While you have the option to pay the full balance by the due date to avoid fees like interest charges, you also have the option to pay a minimum amount or a portion of the balance over time, occurring interest on the remaining balance.
Rewards and benefits
Credit cards come with rewards and benefits that incentivize card usage. These rewards may include cashback on purchases, points redeemable for travel or merchandise, discounts and access to exclusive perks.
In contrast, debit cards typically don’t offer rewards or benefits beyond basic transactional functionality. Since debit cards access your own funds rather than borrowed money, there’s less incentive to provide rewards or benefits to cardholders.
Interest charges
Credit cards accrue interest on unpaid balances carried over from month to month. Credit card issuers typically apply an annual percentage rate (APR) to outstanding balances, and this rate can be quite high, particularly for individuals with lower credit scores.
When you carry a balance beyond the grace period, interest charges accumulate on the unpaid amount, increasing the overall cost of borrowing.
In contrast, debit cards don’t incur interest charges. Since you’re not borrowing money when you use a debit card, there’s no interest applied to purchases or transactions.
Building credit
Using credit cards allows you to build credit. Making timely payments, keeping balances low relative to credit limits and maintaining a long credit history can positively impact credit scores. Credit card activity is reported to the three credit reporting agencies, which gather information on credit card usage, payment history, credit limits, balances and other relevant data to calculate credit scores.
Conversely, debit cards don’t contribute to the building of credit since transactions are not reported to credit bureaus, and you’re not borrowing any money.
What Factors Should You Consider When Choosing Between a Credit vs. Debit Card?
When deciding between a debit vs. credit card, you should consider several factors to ensure that your chosen option is the best one for you.
- Financial habits: Consider your spending habits. If you prefer to pay with the money you already have and avoid borrowing, a debit card may be the better choice. However, if you’re comfortable with responsibly managing credit, you might enjoy a credit card
- Credit history: If you’re looking to build or improve your credit score, using a credit card responsibly can help you build up your credit profile. On the other hand, if you have struggled with debt in the past, a debit card may be a safer option to avoid accumulating more debt
- Rewards and benefits: If you value earning rewards on your spending and can pay off your balance in full each month, a credit card with attractive rewards may be more beneficial. However, if rewards aren’t a priority and you prefer simplicity, you might choose a debit card
- Security and fraud protection: Credit cards typically offer robust fraud protection and zero-liability policies, offering greater peace of mind in case of unauthorized transactions. Many debit cards offer similar protections, but fraud can result in temporary holds on funds in your checking account
- Budgeting and spending control: If you struggle with impulse purchases or tend to overspend with credit, using a debit card may help you create a better budget and stick to it. However, if you prefer the convenience of a credit card for certain purchases or emergencies and can manage spending responsibly, a credit card may offer more flexibility
Still need help deciding? Take advantage of our financial counseling services to help you manage your finances.
Wrapping Up: Understanding Debit vs. Credit
Understanding the difference between debit and credit cards can help you make better financial decisions. At California Credit Union, we understand the importance of options catering to your needs. We offer both credit and debit cards to our members. Whether you prefer the convenience and budgeting control of a debit card or the flexibility and rewards of a credit card, we have options to help you manage your finances effectively and achieve your financial goals.





